

























|
Ritchey-Chrétien Telescope Design


George Willis Ritchey
The Ritchey-Chrétien Telescope was developed jointly by American
optician George Willis Ritchey and French optical designer Henri Chrétien
in the early 1910's. Ritchey, who built the 60 and 100-inch mirrors for Mt. Wilson
observatory, was so upset by the refusal to use the Ritchey-Chrétien
design for the Wilson 100-inch that he publicly criticized it, saying it would be a
spectacular failure, after devoting six years of painstaking work to create it. Ritchey
was fired by Mt. Wilson observatory over this and was essentially banished from American
astronomy. George Ellery Hale refused to even consider this design for the 200-inch on Mt.
Palomar simply because it had Ritchey's name on it, he went with a Classic Cassegrain
instead. History, however, has sided with Ritchey as Kitt Peak, Mauna Kea, Cerro Tololo,
the VLT, and the Hubble Space Telescope - basically every large telescope built or
designed since the 200-inch has used the Ritchey-Chrétien design.
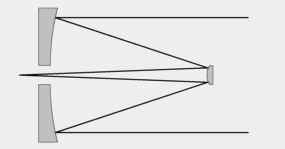
This telescope was designed to produce better images over a large photographic field. Coma
makes it harder to measure star positions, and the Ritchey-Chrétien is coma-free,
producing round stars over the entire field.
The hyperbolic surfaces on both mirrors are not for the faint of heart. These curves are
hard to produce and test. Unless you plan on doing photography and measuring star
positions (astrometery) there is little reason for choosing the difficulty of this design.
The degree of field curvature is related to the difference in radii between the primary
and secondary mirrors. A system with a flat field is possible, but requires a very fast
primary with a deep, difficult to figure curve. The short focal length of the primary then
dictates a large secondary causing more than 50% central obstruction.
With a correcting lens at the focal plane it is possible to simultaneously correct both
astigmatism and curvature of field. This results in an essentially aberration-free
telescope, provided the corrector itself introduces no spherical or chromatic aberration.
This is the design used in the Hubble Space Telescope.
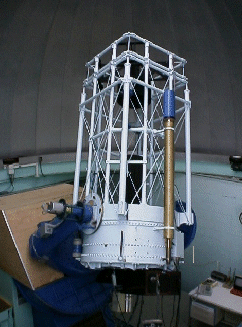
1 Meter Ritchey-Chrétien
Reflector
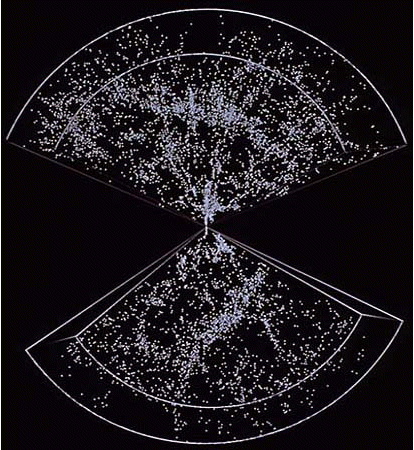
North and South, Sheets and Voids
Stellar maps, published in 1986, were a great surprise to the astrophysicists. They had
expected to find relative uniformity above the scale of the already-familiar galaxy
clusters. Instead, the first surveys showed--and subsequent surveys have confirmed--that
great clusters of galaxies are arranged in thin sheets or long filaments. The longest
sheet detected, called the "Great Wall," extends hundreds of millions of light
years across the maps.
Large-scale structure in the universe in the northern and southern galactic
hemispheres. Each of the 9,325 points in this image represents a galaxy. The Earth lies at
the center; unmapped regions to the top and bottom are inaccessible because the plane of
the Milky Way obscures them. Note the large-scale patterns in both hemispheres, like the
Great Wall stretching across the northern hemisphere. (Courtesy: Margaret
J. Geller and Emilio E. Falco, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Credits:
Geller, da Costa, Huchra, and Falco.)
An antique refractor
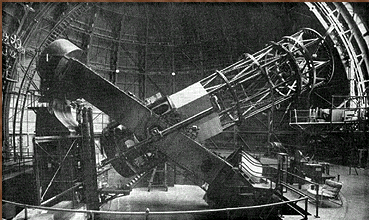
The
100-inch Hooker Telescope
The site of some of the most important advances in the history of astronomy, this
telescope was named after John D. Hooker who donated the cost of the mirror. This
telescope was the largest in the world for thirty years after it opened in November, 1917.
It is a mechanical masterpiece and was dedicated as an International Historical Mechanical
Engineering Landmark in 1981 by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, only the
fourth such award in the United States.
|

